computer_basics:operating_system_fundamentals
Operating System Fundamentals
Adapted from:
LaBerta, Catherine. “System Software.” In Computers Are Your Future. 11th ed. Boston: Prentice Hall., 2010
Mithat Konar
Dec. 4, 2019
The Operating System
- The operating system (OS) is a set of programs that coordinates:
- Hardware functions
- Interaction between application software and computer hardware
The Operating System
- Five basic OS functions:
- Starting the computer
- Managing applications
- Managing memory
- Handling input and output device messages
- Providing a user interface for communication
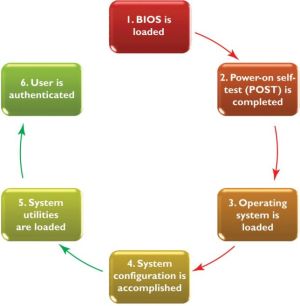
OS function 1: Starting the computer
- OS's first job is to load itself into RAM
- Called booting.
OS function 1: Starting the computer
Booting step 1: BIOS and EFI
- Many computers use a BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) to begin the booting process.
- The first thing that is loaded into memory and starts running when you turn on.
- Manages some core hardware settings.
- Handles the very first stages of the booting process.
- Usually stored in flash memory or CMOS memory chip.
Booting step 1: BIOS and EFI
- Most newer desktops and laptops use EFI (Extensible Firmware Interface) instead of a BIOS.
- UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) is one example.
- Like a mini OS.
- Does everything BIOS does.
- Lets user run small utility applications that run on the Extensible Firmware Interface.
- Considered more secure than traditional BIOS.
Booting step 2: Test the hardware
- Many BIOS/EFIs initiate a power-on self-test (POST) or similar test.
- Confirms that both the computer and its peripheral devices are working properly.
Booting step 3: Load the operating system
- BIOS or EFI loads an OS's kernel into memory.
- kernel: the central part of the OS.
- Usually stored on main storage device.
- The OS then loads remainder of what's needed.
Booting step 4: Check the system configuration
- The OS checks the system configuration for device drivers.
- device driver: utility program that enables communication between the OS and a peripheral device.
- The OS installs and loads the needed drivers.
Booting step 5: Load system utilities
- Antivirus software
- Speaker volume control
- Etc.
Booting step 6: Authenticate user
- Final part of booting is to facilitate user authentication or login.
- Typically a user name and password or fingerprint scan or special code.
OS function 2: Managing applications
- Multitasking operating systems permit more than one application to run at the same time.
- The foreground application is the active one.
- The background applications appear inactive.
OS function 3: Managing memory
- The OS
- gives each program a portion of RAM memory.
- keeps them from interfering with each other.
OS function 3: Managing memory
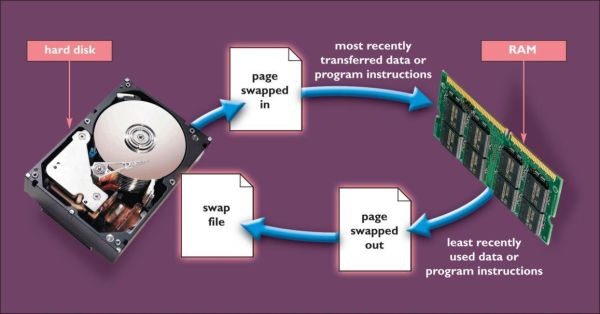
- RAM is organized into pages: units of large fixed size.
- Virtual memory uses a portion of the hard disk to extend RAM.
- When RAM is full, the contents of the most inactive page or pages are temporarily moved to a swap file, a special hard disk file.
- When the page is again needed, it is transferred back into RAM.
- Transferring files between RAM and the hard disk is called paging.
Virtual memory
OS function 3: Managing memory
- Adding more RAM is often a good way to improve computer performance because:
- Paging slows the computer.
- Accessing data from the hard disk is slower than accessing it from RAM.
OS function 4: Handling input and output
- Applications access input and output devices via the OS.
- Device drivers enable communication between the OS and input and output (and other) devices.
OS function 5: Provide a user interface
- The user interface allows the user to:
- Start application programs
- Manage storage devices
- Safely shut down the computer
- Perform other interactions
User interfaces
OS function 5: Provide a user interface
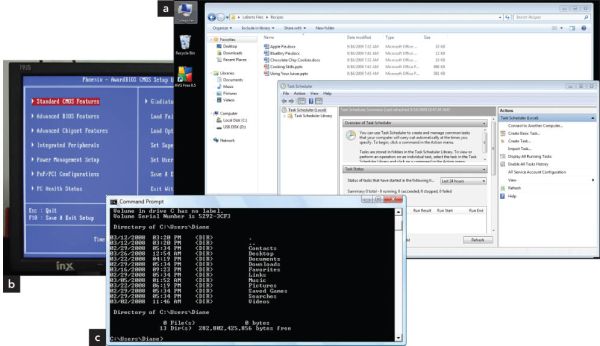
- Types of user interfaces:
- graphical user interface (GUI) uses icons and other visual metaphors.
- menu-driven interface:
- Provides text-based menus.
- Displays available user options.
- command-line interface:
- Requires the user to type commands to instruct the OS to perform the desired actions.
computer_basics/operating_system_fundamentals.txt · Last modified: 2019/12/06 05:11 by mithat