Table of Contents
Windows Python post-install
Or, what to do right after installing Python in Windows
This was written in 2011. It may or may not be accurate today.
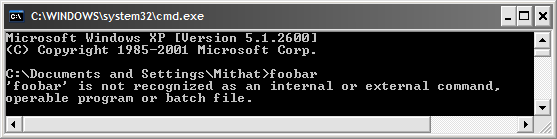
The most common problem with installing Python in Windows is that the installer does not place the Python installation directory on the Path.1) The Path is an environment variable that contains a list of directories that contain the executables that should be used as system commands. In other words, executables located in directories mentioned in the Path can be invoked at the command line using just the name of the executable (e.g., foobar) rather than having to reference the location of the executable (e.g., C:\Some folder\that has\foobar.exe).
So, when you try to run commands, Windows looks in the directories listed in the Path to find an executable with that name. If it finds it, it runs it. If it does not, it gives you the error shown below:
Adding the directory that contains the python command to the Path is not difficult, but it's a little different for each version of Windows. Don't be afraid. As a budding programmer, this is something that you'll need to learn sooner or later, so you may as well learn how to do it now.
Here's how to do it in Windows XP:
- Figure out the directory where Python was installed. At the time of this writing, this will almost certainly be
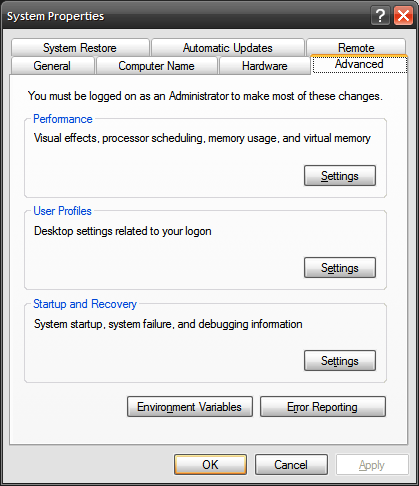
C:\Python27unless you (1) told the installer to place Python somewhere else or (2) installed a version of Python newer (or older) than 2.7. Open up an Explorer window to confirm the directory that Python is in and make a note of it. - Open the Windows XP Control Panel and then open the “System” panel. (Alternately, you can right-click on “My Computer” on the desktop and select “Properties”.)
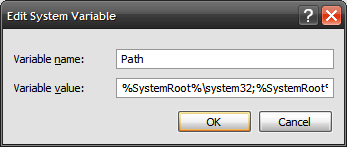
- The list that appears in the lower text area (“Variable value:”) is the list of directories that Windows will look in for system commands (i.e., the Path). We need to add the directory where Python was installed to the end of the list. Scan to the very, very end of the text in the text area and then add
;C:\Python27
or the name of the directory where Python was installed if different from the above.
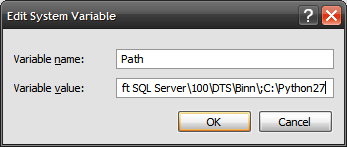
Note: the semicolon is not a typo! Directories in the Path are separated by semicolons. - Click “OK” until all the dialog boxes are closed, and you're done.
Notes
There is a ShowMeDo video that goes through the steps as well, but it's for an older version of Python, so be sure to change the name of the directory to the one your computer is using.
The process for Windows Vista and Windows 7 is very similar but not identical.
Post-uninstall
If you decide to uninstall Python, remember to remove from the Path the Python directory you added above.